Difference between revisions of "CD22"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== CFG Participating Investigators contributing to the understanding of this paradigm == | == CFG Participating Investigators contributing to the understanding of this paradigm == | ||
| − | + | Participating Investigators (PIs) of the CFG have made major contributions to the understanding of the biology of human and murine CD22. These include: | |
| − | Participating Investigators (PIs) of the CFG have made major contributions to the understanding of the biology of human and murine CD22. These include: Nicolai Bovin | + | * Nicolai Bovin |
| + | * Paul Crocker | ||
| + | * Jamey Marth | ||
| + | * David Nemazee | ||
| + | * Lars Nitschke | ||
| + | * Jim Paulson | ||
| + | * Ajit Varki. | ||
== Progress toward understanding this GBP paradigm == | == Progress toward understanding this GBP paradigm == | ||
| Line 40: | Line 46: | ||
! align="center" bgcolor="C0C0F0" colspan="5"|'''CFG database search results for CD22''' | ! align="center" bgcolor="C0C0F0" colspan="5"|'''CFG database search results for CD22''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|'''Resources''' |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|'''Data''' |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|'''Molecule Pages''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=resources&query=CD22 All] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=data&query=CD22 All] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=molpages&query=CD22 All] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?query=CD22&cat=reagents Reagents] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=data&subcat=corec&query=CD22 Glycan profiling] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=molpages&subcat=glycandb&query=CD22 Glycan structures] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?query=CD22&cat=mouselines Mouse lines] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=data&subcat=coree&query=CD22 Glycogene microarray] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=molpages&subcat=cbp&query=CD22 GBP molecules] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?query=CD22&cat=resourcerequest Resource requests] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=data&subcat=coreg&query=CD22 Mouse phenotyping] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=molpages&subcat=gt&query=CD22 Glycosyltransferases] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?query=CD22&cat=otherresources Other resources] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"|[http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?cat=data&subcat=coreh&query=CD22 Glycan array] |
| − | | width=" | + | | width="150" align="center"| |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 73: | Line 79: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| − | + | == Wiki contributors == | |
| + | The CFG is grateful to the PIs for their contributions to this wiki page: Paul Crocker, James Paulson | ||
Revision as of 19:30, 23 March 2010
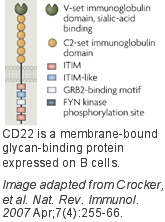
CD22 is predominately expressed on B cells and is well documented as a regulator of B cell receptor (BCR) signaling[1]. It is one of four siglecs that are highly conserved among mammals. This paradigm is unique among the siglecs in that the cytoplasmic domain has six conserved tyrosine motifs, including three immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motifs (ITIM), one ITIM-like motif, and a growth factor receptor bound protein2 (GRB2) motif. These tyrosine motifs are involved in regulation of BCR signaling and also mediate its constitutive clathrin mediated endocytosis, an activity believed to be tied to its regulation of cell signaling. The preferred glycan ligand of CD22 differs significantly in humans and mice[1][2][3]. While both recognize the sequence Siaa-2-6Galb-1-4GlcNAc expressed abundantly on B cells, murine CD22 prefers Neu5Gc (not found in humans) over Neu5Ac, while human CD22 exhibits highest affinity for sulfated sialoside, Neu5Aca-2-6Galb-1-4[6S]GlcNAc, demonstrating significant evolution of ligand specificity with conservation of function. Although CD22 recognizes ligands on the same cell in cis, it also binds to ligands in trans if expressed on adjacent contacting cells. A major area of investigation is to understand the relative roles of cis and trans ligands in CD22 function.
CFG Participating Investigators contributing to the understanding of this paradigm
Participating Investigators (PIs) of the CFG have made major contributions to the understanding of the biology of human and murine CD22. These include:
- Nicolai Bovin
- Paul Crocker
- Jamey Marth
- David Nemazee
- Lars Nitschke
- Jim Paulson
- Ajit Varki.
Progress toward understanding this GBP paradigm
Carbohydrate ligands
Cellular expression
Structure
Biological roles of GBP-ligand interaction
CFG resources used in investigations
Glycan profiling
Glycogene microarray
The CFG glycogene microarray has been used to show that the ligands of CD22 are downregulated upon B cell activation.
Knockout mouse lines
Mice deficient in CD22 and the sialyltransferase responsible for synthesis of its ligands (ST6Gal I) distributed by the CFG have been instrumental in understanding the biology of CD22.
Glycan array
The glycan microarray of the CFG was instrumental in identification of the high affinity ligand of CD22 as a sialylated-sulfated glycan.
| CFG database search results for CD22 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resources | Data | Molecule Pages | ||
| All | All | All | ||
| Reagents | Glycan profiling | Glycan structures | ||
| Mouse lines | Glycogene microarray | GBP molecules | ||
| Resource requests | Mouse phenotyping | Glycosyltransferases | ||
| Other resources | Glycan array | |||
Related GBPs
None. This paradigm is unique among the siglecs in that the cytoplasmic domain has 6 conserved tyrosine motifs, including 3 immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motifs (ITIM), one ITIM-like motif, and a growth factor receptor bound protein2 (GRB2) motif.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Crocker PR, Paulson JC, Varki A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2007 Apr;7(4):255-66. Review.
- ↑ Kimura N, Ohmori K, Miyazaki K, Izawa M, Matsuzaki Y, Yasuda Y, Takematsu H, Kozutsumi Y, Moriyama A, Kannagi R. Human B-lymphocytes express alpha2-6-sialylated 6-sulfo-N-acetyllactosamine serving as a preferred ligand for CD22/Siglec-2. J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):32200-7.
- ↑ Blixt O, Head S, Mondala T, Scanlan C, Huflejt ME, Alvarez R, Bryan MC, Fazio F, Calarese D, Stevens J, Razi N, Stevens DJ, Skehel JJ, van Die I, Burton DR, Wilson IA, Cummings R, Bovin N, Wong CH, Paulson JC. Printed covalent glycan array for ligand profiling of diverse glycan binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17033-8.
Wiki contributors
The CFG is grateful to the PIs for their contributions to this wiki page: Paul Crocker, James Paulson