Difference between revisions of "Siglec-8"
Jim Paulson (talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | === Cellular expression === | + | === Cellular expression of GBP and ligands === |
Human: Eosinophils, Mast Cells, Basophils (weak)<ref>Kikly KK, Bochner BS, Freeman S, Tan KB, Gallagher KT, D'Alessio K, Holmes SD, Abrahamson J, Hopson CB, Fischer EI, Erickson-Miller CL, Tachimoto H, Schleimer RP, White JR. Identification of SAF-2, a novel siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105:1093-100</ref><ref>Floyd H, Ni J, Cornish AL, Zeng Z, Liu D, Carter KC, Steel J, Crocker PR. Siglec-8: a novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:861-6</ref><ref>Yokoi H, Myers A, Matsumoto K, Crocker PR, Saito H, Bochner BS. Alteration and acquisition of Siglecs during in vitro maturation of CD34+ progenitors into human mast cells. Allergy 2006; 61:769-76</ref> | Human: Eosinophils, Mast Cells, Basophils (weak)<ref>Kikly KK, Bochner BS, Freeman S, Tan KB, Gallagher KT, D'Alessio K, Holmes SD, Abrahamson J, Hopson CB, Fischer EI, Erickson-Miller CL, Tachimoto H, Schleimer RP, White JR. Identification of SAF-2, a novel siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105:1093-100</ref><ref>Floyd H, Ni J, Cornish AL, Zeng Z, Liu D, Carter KC, Steel J, Crocker PR. Siglec-8: a novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:861-6</ref><ref>Yokoi H, Myers A, Matsumoto K, Crocker PR, Saito H, Bochner BS. Alteration and acquisition of Siglecs during in vitro maturation of CD34+ progenitors into human mast cells. Allergy 2006; 61:769-76</ref> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | === Biosynthesis of ligands === | |
| + | <br> | ||
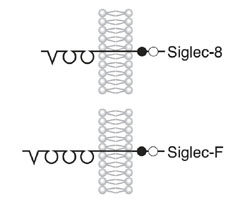
=== Structure === | === Structure === | ||
[[File:Siglec8 SiglecF.jpg]] | [[File:Siglec8 SiglecF.jpg]] | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
=== Glycan array === | === Glycan array === | ||
| − | The discovery of the ligand for Siglec-8[http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v3_49_09152004][http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v2_19_02202004] and its murine paralog, Siglec-F[http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v3_47_10132004][http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v2_58_07262004], was made by investigator-initiated resource requests for glycan array analysis and carbohydrate compounds. | + | The discovery of the ligand for Siglec-8[http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v3_49_09152004][http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v2_19_02202004] and its murine paralog, Siglec-F[http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v3_47_10132004][http://www.functionalglycomics.org:80/glycomics/HServlet?operation=view&sideMenu=no&psId=primscreen_GLYCAN_v2_58_07262004], was made by investigator-initiated resource requests for glycan array analysis and carbohydrate compounds. To see all glycan array results for Siglec-8, click [http://www.functionalglycomics.org/glycomics/search/jsp/result.jsp?query=siglec-8&cat=coreh here]. |
== Related GBPs == | == Related GBPs == | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 21 June 2010
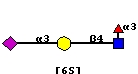
Siglec-8 is a human siglec expressed predominantly on eosinophils and mast cells, and is a paradigm for the rapidly evolving sub-family of CD33-related siglecs that are expressed on various white blood cells[1][2][3][4]. A characteristic feature of Siglec-8 and most other CD33-related siglecs is a cytoplasmic domain with a single immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motif (ITIM) and a single ITIM-like motif that participate in siglec-mediated regulation of cell signaling and endocytosis. While there is no clear ortholog in mice, Siglec-F has been documented as a functional paralog that has a similar expression pattern on murine leukocytes and similar ligand specificity[3][5][6]. Siglec-8, and its murine paralog Siglec-F, recognize a ligand containing both sialic acid and sulfate (NeuAcα2-3[6S]Galβ1-4G[Fucα1-3]GlcNAc-), a specificity that is distinct from all other siglecs. Ligation of Siglec-8 (or Siglec-F) with antibodies or polymeric ligands induces apoptosis of eosinophils, suggesting a therapeutic approach for treating eosinophil (or mast cell) mediated disease by targeting Siglec-8[7][8][9][10].
CFG Participating Investigators contributing to the understanding of this paradigm
Participating Investigators (PIs) of the CFG have made major contributions to the understanding of the biology of Siglec-8 and its murine paralog, Siglec-F. These include: Bruce Bochner, Nicolai Bovin, Paul Crocker, James Paulson, Ronald Schnaar, Ajit Varki
Progress toward understanding this GBP paradigm
Carbohydrate ligands
The high affinity ligand for Siglec-8 has been deduced from glycan microarray screening on the CFG microarray[1][2] to be NeuAcα2-3(6-SO3)Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)GlcNAc [6'Su-SLeX][11][12]
For Siglec-F, histologic studies suggest the presence of an α2,3-linked sialylated glycoprotein ligand expressed by airway epithelium. Its constitutive expression requires the enzyme St3Gal3.[13] Levels of this ligand are increased during allergic pulmonary inflammation.[14]
Cellular expression of GBP and ligands
Human: Eosinophils, Mast Cells, Basophils (weak)[15][16][17]
Biosynthesis of ligands
Structure
Biological roles of GBP-ligand interaction
In vitro Eosinophil apoptosis.[18][19][20] Inhibition of mast cell mediator release.[21]
In vivo (for Siglec-F)
Antibody administration to mice causes selective depletion of eosinophils in blood and gastrointestinal tissues via apoptosis.[22] They are also effective in reversing some sequelae of mouse models of eosinophilic gastroenteritis and asthma.[23][24]
CFG resources used in investigations
The best examples of CFG contributions to this paradigm are described below, with links to specific data sets. For a complete list of CFG data and resources relating to this paradigm, see the CFG database search results for Siglec-8.
Glycan profiling
Glycan structure analysis has been conducted by the CFG for human[3] and mouse[4] eosinophils.
Glycogene microarray
Analysis has been conducted on glycosyltransferase expression using the glycogene microarray for murine eosinophils that relates to the enzymes required for expression of cis ligands of Siglec-F on these cells[5].
Knockout mouse lines
Mice deficient in Siglec-F have normal blood and bone marrow eosinophils at baseline, but develop exaggerated bone marrow, blood and lung eosinophilia after allergen sensitization and challenge.[25]
Glycan array
The discovery of the ligand for Siglec-8[6][7] and its murine paralog, Siglec-F[8][9], was made by investigator-initiated resource requests for glycan array analysis and carbohydrate compounds. To see all glycan array results for Siglec-8, click here.
Related GBPs
hSiglec-3 (CD33), Siglec-5, Siglec-6, Siglec, 7, Siglec-9, Siglec-10, Siglec-11, Siglec-F, Siglec-E, Siglec-G
References
- ↑ Crocker, P. R., Paulson, J. C. & Varki, A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 7, 255-266 (2007).
- ↑ Kikly, K.K., Bochner, B.S., et al. Identification of SAF-2, a novel siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105, 1093-100 (2000)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bochner, B.S. Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally related inhibitory receptors. Clin Exp Allergy 39, 317-324 (2009).
- ↑ Floyd, H. et al. Siglec-8. A novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 275, 861-866 (2000).
- ↑ Tateno, H., Crocker, P. R. & Paulson, J. C. Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6'-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand. Glycobiology 15, 1125-1135 (2005).
- ↑ Zhang, M. et al. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood 109, 4280-4287 (2007).
- ↑ O'Reilly, M. K. & Paulson, J. C. Siglecs as targets for therapy in immune-cell-mediated disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30, 240-248 (2009).
- ↑ Zimmermann, N. et al. Siglec-F antibody administration to mice selectively reduces blood and tissue eosinophils. Allergy 63, 1156-1163 (2008).
- ↑ Bochner, B. S. et al. Glycan array screening reveals a candidate ligand for Siglec-8. J Biol Chem 280, 4307- 4312 (2005).
- ↑ Nutku, E., Aizawa, H., Hudson, S. A. & Bochner, B. S. Ligation of Siglec-8: a selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis. Blood 101, 5014-5020 (2003).
- ↑ Bochner BS, Alvarez RA, Mehta P, Bovin NV, Blixt O, White JR, Schnaar RL. Glycan array screening reveals a candidate ligand for Siglec-8. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:4307-12
- ↑ Tateno H, Crocker PR, Paulson JC. Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6'-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand. Glycobiology 2005; 15:1125-35
- ↑ Guo JP, Brummet ME, Myers AC, Na HJ, Rowland E, Schnaar RL, Zheng T, Zhu Z, Bochner BS. Characterization of expression of glycan ligands for Siglec-F in normal mouse lungs. Am J Respir Cell and Molec Biol 2010 Apr 15 [Epub ahead of print] 2010 and
- ↑ Zhang M, Angata T, Cho JY, Miller M, Broide DH, Varki A. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood 2007; 109:4280-7
- ↑ Kikly KK, Bochner BS, Freeman S, Tan KB, Gallagher KT, D'Alessio K, Holmes SD, Abrahamson J, Hopson CB, Fischer EI, Erickson-Miller CL, Tachimoto H, Schleimer RP, White JR. Identification of SAF-2, a novel siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105:1093-100
- ↑ Floyd H, Ni J, Cornish AL, Zeng Z, Liu D, Carter KC, Steel J, Crocker PR. Siglec-8: a novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:861-6
- ↑ Yokoi H, Myers A, Matsumoto K, Crocker PR, Saito H, Bochner BS. Alteration and acquisition of Siglecs during in vitro maturation of CD34+ progenitors into human mast cells. Allergy 2006; 61:769-76
- ↑ Nutku E, Aizawa H, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Ligation of Siglec-8: a selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis. Blood 2003; 101:5014-20
- ↑ Nutku E, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Mechanism of Siglec-8-induced human eosinophil apoptosis: role of caspases and mitochondrial injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 336:918-24
- ↑ 1Nutku-Bilir E, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Interleukin-5 priming of human eosinophils alters Siglec-8 mediated apoptosis pathways. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2008; 38:121-4
- ↑ Yokoi H, Choi OH, Hubbard W, Lee H-S, Canning BJ, Lee HH, Ryu S-D, Bickel CA, Hudson SA, MacGlashan DW, Jr., Bochner BS. Inhibition of FcεRI-dependent mediator release and calcium flux from human mast cells by Siglec-8 engagement. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121:499-505
- ↑ Zimmermann N, McBride ML, Yamada Y, Hudson SA, Jones C, Cromie KD, Crocker PR, Rothenberg ME, Bochner BS. Siglec-F antibody administration to mice selectively reduces blood and tissue eosinophils. Allergy 2008; 63:1156-63
- ↑ Song DJ, Cho JY, Miller M, Strangman W, Zhang M, Varki A, Broide DH. Anti-Siglec-F antibody inhibits oral egg allergen induced intestinal eosinophilic inflammation in a mouse model. Clin Immunol 2009; 131:157-69
- ↑ Song DJ, Cho JY, Lee SY, Miller M, Rosenthal P, Soroosh P, Croft M, Zhang M, Varki A, Broide DH. Anti-Siglec-F antibody reduces allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation and airway remodeling. J Immunol 2009; 183:5333-41
- ↑ Zhang M, Angata T, Cho JY, Miller M, Broide DH, Varki A. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood 2007; 109:4280-7
Acknowledgements
The CFG is grateful to the following PIs for their contributions to this wiki page: Bruce Bochner, Paul Crocker, James Paulson, Ron Schnaar