Siglec-8
Siglec-8 is a human siglec expressed predominantly on eosinophils and mast cells, and is a paradigm for the rapidly evolving sub-family of CD33-related siglecs that are expressed on various white blood cells[1][2][3][4]. A characteristic feature of Siglec-8 and most other CD33-related siglecs is a cytoplasmic domain with a single immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motif (ITIM) and a single ITIM-like motif that participate in siglec-mediated regulation of cell signaling and endocytosis. While there is no clear ortholog in mice, Siglec-F has been documented as a functional paralog that has a similar expression pattern on murine leukocytes and similar ligand specificity[3][5][6]. Siglec-8, and its murine paralog Siglec-F, recognize a ligand containing both sialic acid and sulfate (NeuAcα2-3[6S]Galβ1-4G[Fucα1-3]GlcNAc-), a specificity that is distinct from all other siglecs. Ligation of Siglec-8 (or Siglec-F) with antibodies or polymeric ligands induces apoptosis of eosinophils, suggesting a therapeutic approach for treating eosinophil (or mast cell) mediated disease by targeting Siglec-8[7][8][9][10].
CFG Participating Investigators contributing to the understanding of this paradigm
Participating Investigators (PIs) of the CFG have made major contributions to the understanding of the biology of Siglec-8 and its murine paralog, Siglec-F. These include: Bruce Bochner, Nicolai Bovin, Paul Crocker, James Paulson, Ronald Schnaar, Ajit Varki
Progress toward understanding this GBP paradigm
Carbohydrate ligands
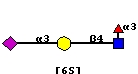
The high affinity ligand for siglec-8 has been deduced from glycan microarray screening on the CFG microarray to be NeuAcα2-3(6-SO3)Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)GlcNAc [6'Su-SLeX][11][12]
For Siglec-F, histologic studies suggest the presence of an α2,3-linked sialylated glycoprotein ligand expressed by airway epithelium. Its constitutive expression requires the enzyme St3Gal3.[13] Levels of this ligand are increased during allergic pulmonary inflammation.[14]
Cellular expression
Human: Eosinophils, Mast Cells, Basophils (weak)[15][16][17]
Structure
Biological roles of GBP-ligand interaction
In vitro Eosinophil apoptosis.[18][19][20] Inhibition of mast cell mediator release.[21]
In vivo (for Siglec-F)
Antibody administration to mice causes selective depletion of eosinophils in blood and gastrointestinal tissues via apoptosis.[22] They are also effective in reversing some sequelae of mouse models of eosinophilic gastroenteritis and asthma.[23][24]
CFG resources used in investigations
The best examples of CFG contributions to this paradigm are described below, with links to specific data sets. For a complete list of CFG data and resources relating to this paradigm, see the CFG database search results for Siglec-8.
Glycan profiling
Glycan structure analysis has been conducted by the CFG for human and mouse eosinophils.
Glycogene microarray
Analysis has been conducted on glycosyltransferase expression using the glycogene microarray for murine eosinophils.
Knockout mouse lines
Mice deficient in Siglec-F have normal blood and bone marrow eosinophils at baseline, but develop exaggerated bone marrow, blood and lung eosinophilia after allergen sensitization and challenge.[25]
Glycan array
The discovery of the ligand for siglec-8 and its murine paralog, Siglec-F, was made by investigator-initiated resource requests for glycan array analysis and carbohydrate compounds.
Related GBPs
hSiglec-3 (CD33), Siglec-5, Siglec-6, Siglec, 7, Siglec-9, Siglec-10, Siglec-11, Siglec-F, Siglec-E, Siglec-G
References
- ↑ Crocker, P. R., Paulson, J. C. & Varki, A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 7, 255-266 (2007).
- ↑ Kikly, K.K., Bochner, B.S., et al. Identification of SAF-2, a novel siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105, 1093-100 (2000)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bochner, B.S. Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally related inhibitory receptors. Clin Exp Allergy 39, 317-324 (2009).
- ↑ Floyd, H. et al. Siglec-8. A novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 275, 861-866 (2000).
- ↑ Tateno, H., Crocker, P. R. & Paulson, J. C. Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6'-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand. Glycobiology 15, 1125-1135 (2005).
- ↑ Zhang, M. et al. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood 109, 4280-4287 (2007).
- ↑ O'Reilly, M. K. & Paulson, J. C. Siglecs as targets for therapy in immune-cell-mediated disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30, 240-248 (2009).
- ↑ Zimmermann, N. et al. Siglec-F antibody administration to mice selectively reduces blood and tissue eosinophils. Allergy 63, 1156-1163 (2008).
- ↑ Bochner, B. S. et al. Glycan array screening reveals a candidate ligand for Siglec-8. J Biol Chem 280, 4307- 4312 (2005).
- ↑ Nutku, E., Aizawa, H., Hudson, S. A. & Bochner, B. S. Ligation of Siglec-8: a selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis. Blood 101, 5014-5020 (2003).
- ↑ Bochner BS, Alvarez RA, Mehta P, Bovin NV, Blixt O, White JR, Schnaar RL. Glycan array screening reveals a candidate ligand for Siglec-8. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:4307-12
- ↑ Tateno H, Crocker PR, Paulson JC. Mouse Siglec-F and human Siglec-8 are functionally convergent paralogs that are selectively expressed on eosinophils and recognize 6'-sulfo-sialyl Lewis X as a preferred glycan ligand. Glycobiology 2005; 15:1125-35
- ↑ Guo JP, Brummet ME, Myers AC, Na HJ, Rowland E, Schnaar RL, Zheng T, Zhu Z, Bochner BS. Characterization of expression of glycan ligands for Siglec-F in normal mouse lungs. Am J Respir Cell and Molec Biol 2010 Apr 15 [Epub ahead of print] 2010 and
- ↑ Zhang M, Angata T, Cho JY, Miller M, Broide DH, Varki A. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood 2007; 109:4280-7
- ↑ Kikly KK, Bochner BS, Freeman S, Tan KB, Gallagher KT, D'Alessio K, Holmes SD, Abrahamson J, Hopson CB, Fischer EI, Erickson-Miller CL, Tachimoto H, Schleimer RP, White JR. Identification of SAF-2, a novel siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 105:1093-100
- ↑ Floyd H, Ni J, Cornish AL, Zeng Z, Liu D, Carter KC, Steel J, Crocker PR. Siglec-8: a novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:861-6
- ↑ Yokoi H, Myers A, Matsumoto K, Crocker PR, Saito H, Bochner BS. Alteration and acquisition of Siglecs during in vitro maturation of CD34+ progenitors into human mast cells. Allergy 2006; 61:769-76
- ↑ Nutku E, Aizawa H, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Ligation of Siglec-8: a selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis. Blood 2003; 101:5014-20
- ↑ Nutku E, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Mechanism of Siglec-8-induced human eosinophil apoptosis: role of caspases and mitochondrial injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 336:918-24
- ↑ 1Nutku-Bilir E, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Interleukin-5 priming of human eosinophils alters Siglec-8 mediated apoptosis pathways. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2008; 38:121-4
- ↑ Yokoi H, Choi OH, Hubbard W, Lee H-S, Canning BJ, Lee HH, Ryu S-D, Bickel CA, Hudson SA, MacGlashan DW, Jr., Bochner BS. Inhibition of FcεRI-dependent mediator release and calcium flux from human mast cells by Siglec-8 engagement. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121:499-505
- ↑ Zimmermann N, McBride ML, Yamada Y, Hudson SA, Jones C, Cromie KD, Crocker PR, Rothenberg ME, Bochner BS. Siglec-F antibody administration to mice selectively reduces blood and tissue eosinophils. Allergy 2008; 63:1156-63
- ↑ Song DJ, Cho JY, Miller M, Strangman W, Zhang M, Varki A, Broide DH. Anti-Siglec-F antibody inhibits oral egg allergen induced intestinal eosinophilic inflammation in a mouse model. Clin Immunol 2009; 131:157-69
- ↑ Song DJ, Cho JY, Lee SY, Miller M, Rosenthal P, Soroosh P, Croft M, Zhang M, Varki A, Broide DH. Anti-Siglec-F antibody reduces allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation and airway remodeling. J Immunol 2009; 183:5333-41
- ↑ Zhang M, Angata T, Cho JY, Miller M, Broide DH, Varki A. Defining the in vivo function of Siglec-F, a CD33-related Siglec expressed on mouse eosinophils. Blood 2007; 109:4280-7
Acknowledgements
The CFG is grateful to the following PIs for their contributions to this wiki page: Bruce Bochner, Paul Crocker, James Paulson, Ron Schnaar